Hemp can help: Nature’s Swiss Army Knife to a Sustainable Future (and it Doesn’t Even Need a Battery Pack)
Let’s face it, folks, the planet needs a makeover. Climate change is doing the Macarena on our glaciers, plastic islands are chilling in the oceans like uninvited guests at a pool party, and the whole “sustainable living” thing can feel about as exciting as watching paint dry.
But fear not, eco-warriors and weary consumers alike! Enter hemp, the world’s most underappreciated superhero with a resume longer than your grocery list. This isn’t your stoner uncle’s cannabis (though hemp’s cooler, cousin can take some credit for the good mood); hemp is a powerhouse plant with the potential to revolutionize our world – and it does it all without needing a cape or a costume change.
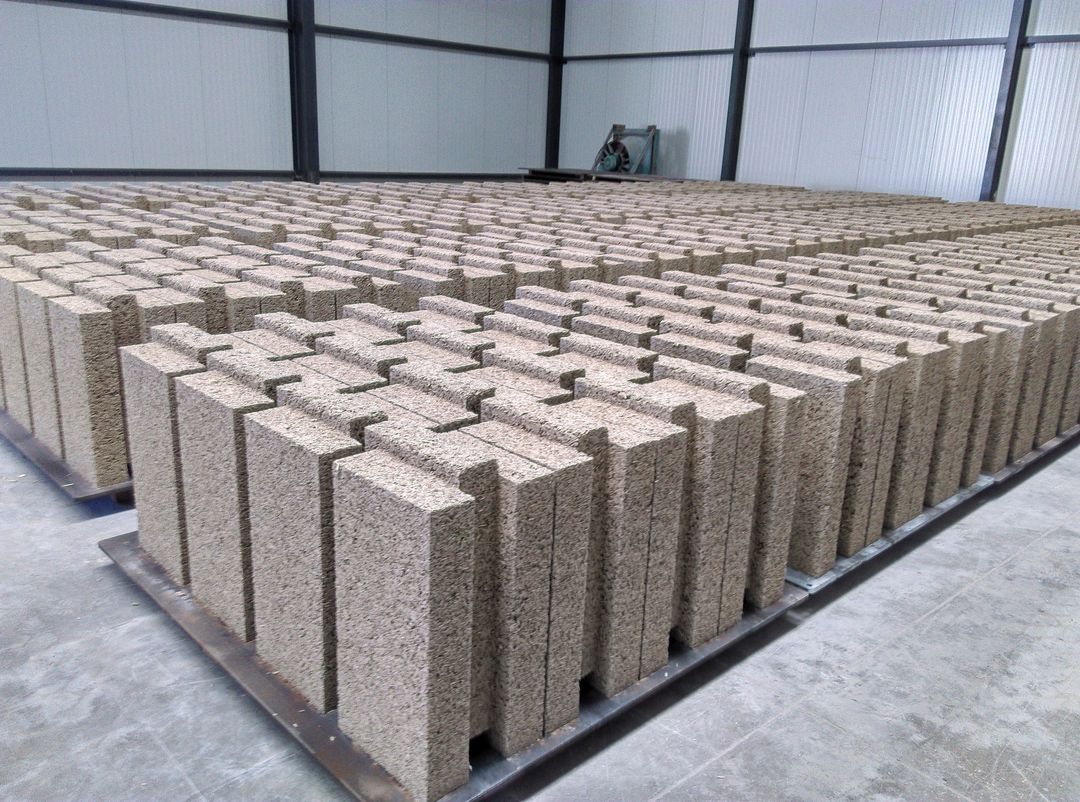
Need clothes that are comfy, stylish, and made from a plant that practically grows itself? Hemp’s got your back (and your legs, and your arms). Craving a building material that’s strong, fire-resistant, and good for the environment? Hemp’s got your roof (and your walls, if you’re feeling adventurous). Looking for a biofuel that doesn’t involve arguing with your spouse at the gas pump? Hemp’s whispering sweet nothings in your gas tank (okay, maybe not literally, but you get the idea).
Hemp’s benefits don’t stop at your carbon footprint. This wonder plant is a nutritional powerhouse, packed with protein and healthy fats that can keep you feeling energized and ready to tackle that overflowing recycling bin. Hemp-derived CBD oil is also gaining traction for its potential to alleviate anxiety, pain, and inflammation, basically turning you into a zen master who can finally compost that banana peel without existential dread.
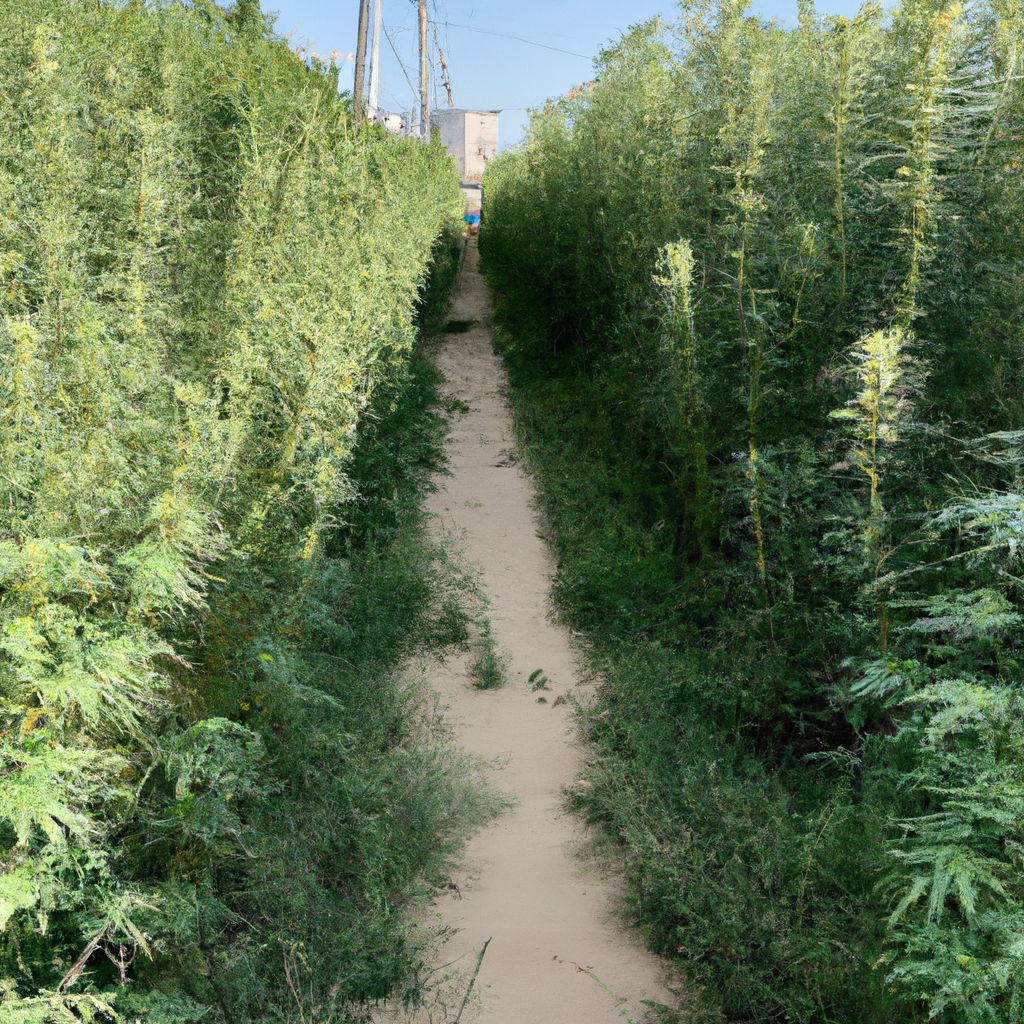
But wait, there’s more! Hemp is a champion of economic equity. Because it requires minimal resources to grow and thrives in various climates, it can empower farmers and create new opportunities in rural communities. This translates to a more vibrant and equitable economy, which means everyone gets to win (except maybe those landfills overflowing with plastic).
So ditch the single-use plastics, swap your sweatpants for some comfy hemp joggers, and consider investing in a hemp-based surfboard (they’re a thing, and they’re awesome). Hemp may not be able to solve world hunger overnight, but it’s a mighty big step towards a future that’s good for the planet, good for our health, and good for our wallets. Hemp can help. Let’s give it a chance.

 | portal.hempnation.one
| portal.hempnation.one![]() Contribute to cleaner air and water quality through carbon sequestration and filtration.
Contribute to cleaner air and water quality through carbon sequestration and filtration.![]() Generate income from hemp production for various purposes such as textiles, construction materials, and biofuels.
Generate income from hemp production for various purposes such as textiles, construction materials, and biofuels.![]() Rejuvenate rural communities by offering sustainable and profitable agricultural options.
Rejuvenate rural communities by offering sustainable and profitable agricultural options.