Hemp: A Sustainable Solution for Construction, Environmental Cleanup, and Energy Storage
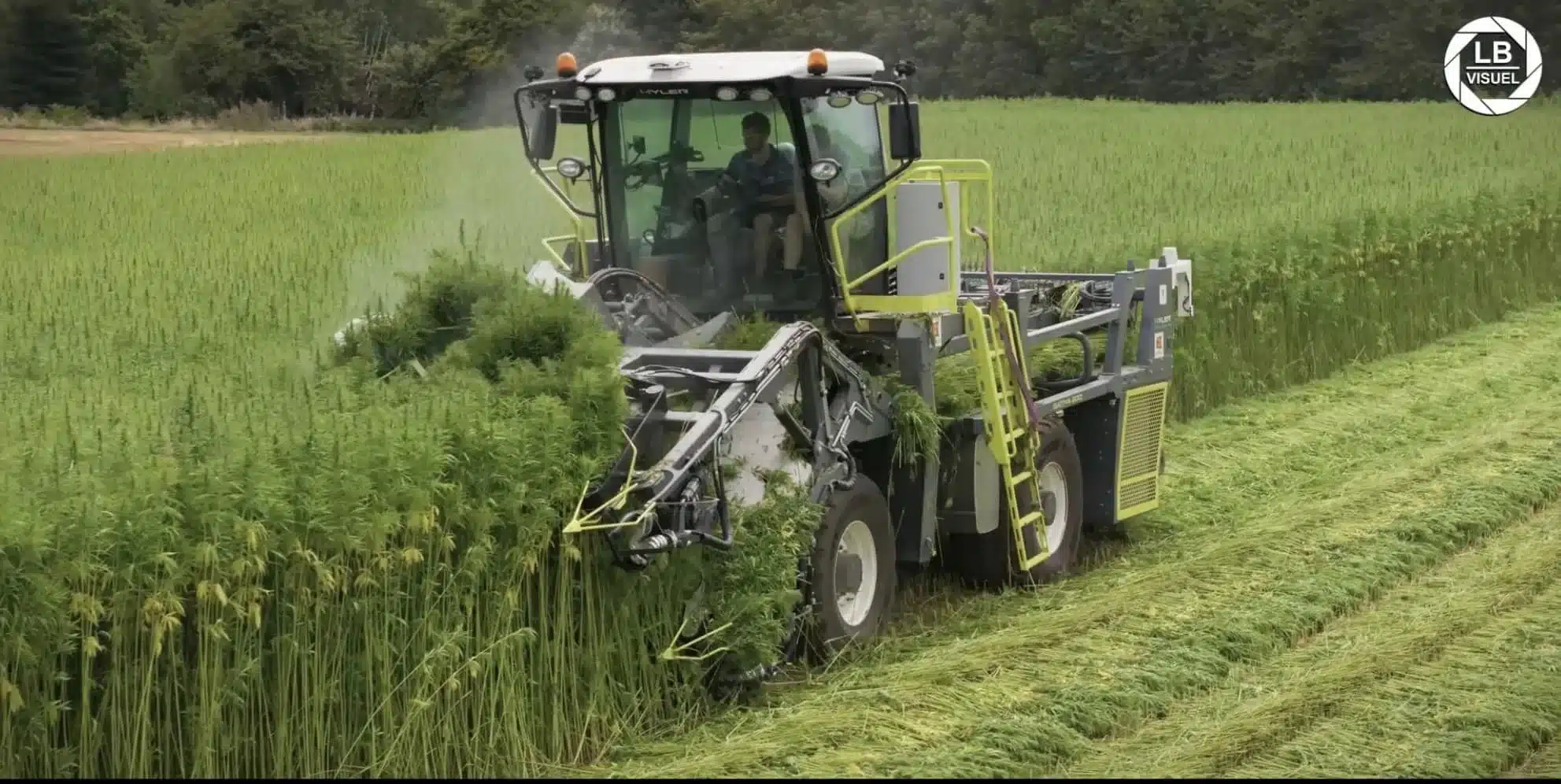
Hemp, a versatile plant with a rich history, is experiencing a resurgence as a sustainable building material and environmental solution. Its rapid growth, robust nature, and ability to absorb carbon dioxide make it an attractive alternative to traditional materials. This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of hemp in construction, environmental cleanup, and energy storage, highlighting its potential to contribute to a more sustainable future.
Construction with Hemp: A Sustainable Building Block
Hempcrete, a composite material made from hemp hurd (the woody core of the hemp stalk) and a lime binder, is gaining popularity in the construction industry. It offers numerous advantages:
- Excellent Insulation: Hempcrete provides exceptional thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling by up to 40%.
- Superior Soundproofing: Its dense cellular structure effectively absorbs sound, reducing noise pollution by up to 20%.
- Fire Resistance: Hempcrete is highly fire-resistant, offering superior protection against fire hazards.
- Moisture Regulation: It can absorb and release moisture, helping to maintain a healthy indoor climate and preventing mold growth.
- Carbon Sequestration: Hempcrete acts as a carbon sink, capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. It can sequester up to 12 tonnes of CO2 per hectare per year.
Environmental Cleanup with Hemp: A Natural Solution
Hemp has the potential to play a significant role in environmental cleanup and remediation:
- Soil Remediation: Hemp can be used to phytoremediate contaminated soil by absorbing heavy metals and pollutants. It can remove pollutants like lead, cadmium, and arsenic from soil.
- Water Filtration: Hemp can be used to filter water, removing pollutants and improving water quality. A single hectare of hemp can absorb 3000 liters of water per day.
- Waste Reduction: Hemp-based products can reduce waste generation and promote a circular economy. The hemp industry generates significantly less waste compared to traditional industries.
Hemp as an Energy Storage Solution
Beyond construction and environmental cleanup, hemp can be utilized in energy storage applications:
- Hempcrete Batteries: Researchers are exploring the possibility of using hempcrete as a matrix for energy storage devices, such as batteries. This could lead to more sustainable and efficient energy storage solutions.
- Bioenergy: Hemp can be converted into biofuels, providing a renewable energy source. One hectare of hemp can produce enough biofuel to power a car for a year.
- Biogas Production: Hemp residues can be used to produce biogas, a clean and renewable energy source. Hemp can produce more biogas per acre than any other crop.
Social, Economic, and Environmental Benefits
The widespread adoption of hemp in construction and other industries can yield significant social, economic, and environmental benefits:
- Job Creation: The global hemp industry employs millions of people worldwide, with potential for significant job growth in the future.
- Economic Growth: The hemp industry contributes billions of dollars to the global economy.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Hemp-based products can reduce carbon emissions and minimize ecological damage. The hemp industry has a significantly lower carbon footprint than traditional industries.
- Improved Health and Well-being: Hemp-based building materials can create healthier and more comfortable living environments.
- Social Equity: The cultivation of hemp can provide opportunities for marginalized communities.
Conclusion
Hemp, a versatile and sustainable resource, offers a promising future for construction, environmental cleanup, and energy storage. By embracing this ancient plant, we can build a more sustainable, resilient, and equitable future.